Introduction:
In the forty years since the Internet was invented, technology has increasingly blurred the lines between the digital world and the three-dimensional world we live in. We have now reached an inflection point where two-dimensional screens and simple information transfer are no longer enough. The new world order requires a new kind of web – the “Spatial Web” — to navigate, map, and enhance our environment.
The real estate industry has historically been slow to adapt to digital technologies, even as online platforms have become essential tools for buyers, sellers, and agents. As the Internet continues to evolve, multi-user experiences enabled by Spatial Web—Web 3.0—are poised to revolutionize the industry. In this piece, we will examine how multi-user experiences can fundamentally transform the process of buying and selling property online.
Outline
I. The Evolution of Real Estate Platforms
- A. Traditional property search methods
- B. Virtual tours and 360-degree views
II. The Spatial Web and Multi-User Experiences
- A. Definition of the Spatial Web
- B. How the Spatial Web enables multi-user experiences
- C. The potential impact on the real estate industry
III. Virtual Property Tours and Open Houses
- A. Interactive, multi-user virtual tours
- B. Advantages of virtual open houses
- C. Enhanced property exploration and customization
IV. Real-Time Collaboration in Real Estate Transactions
- A. Virtual meetings with agents, buyers, and sellers
- B. Real-time document sharing and contract negotiation
- C. Streamlining the closing process
V. Augmented and Virtual Reality for Property Visualization
- A. AR/VR integration in real estate platforms
- B. Immersive property staging and interior design
- C. Visualizing property development and construction projects
VI. Building Virtual Communities and Social Engagement
- A. Virtual neighborhood tours and community exploration
- B. Connecting potential buyers and residents
- C. Leveraging social media and virtual events for marketing
VII. Challenges and Limitations
- A. Technological barriers and infrastructure
- B. Privacy and security concerns
- C. Ensuring a seamless user experience
I. The Evolution of Real Estate Platforms
A. Traditional property search methods
It’s hard to remember a time when real estate transactions happened without the help of property websites like Zillow, Trulia, and Realtor.com that allows buyers to search by location, price, size, and must-have features. Before the Internet, potential property buyers scanned hardcopy newspaper Classified sections, visited real estate agencies in-person, and were often limited to word-of-mouth or outdated manual advertising. Now sellers and agents have multi-channel marketing options to reach a wide audience and can showcase their properties through high-definition imagery and detailed descriptions.
B. Virtual tours and 360-degree views
As technology has advanced and the world shrunk, apartment seekers increasingly start their search remotely and have come to expect features like virtual tours and 3D walkthroughs. Interactive features like 360-degree views allow users to virtually walk through a property and explore its layout, features, and surroundings. This innovation reduced the need for in-person visits, saving time and resources for both buyers and sellers. Now the Spatial Web is poised to revolutionize property platforms further by introducing multi-user experiences.
II. The Spatial Web and Multi-User Experiences

A. Definition of the Spatial Web
Imagine a seamless, interactive digital environment overlaid onto the physical world. Spatial Web is an envisioned not-so-distant future where the virtual and physical realities overlay each other as twins in three-dimensional space, enabled by Web 3.0 technology. That includes spatial computing technology, like augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR), but also physical world technology like Internet of Things (IoT) and robotic sensors. Artificial intelligence (AI) is quickly surpassing human programming, making everything “smarter” faster. Add on decentralized computing and blockchain, and you have an unimaginably rich environment that breaks the barriers of traditional web interaction.

B. How the Spatial Web enables multi-user experiences
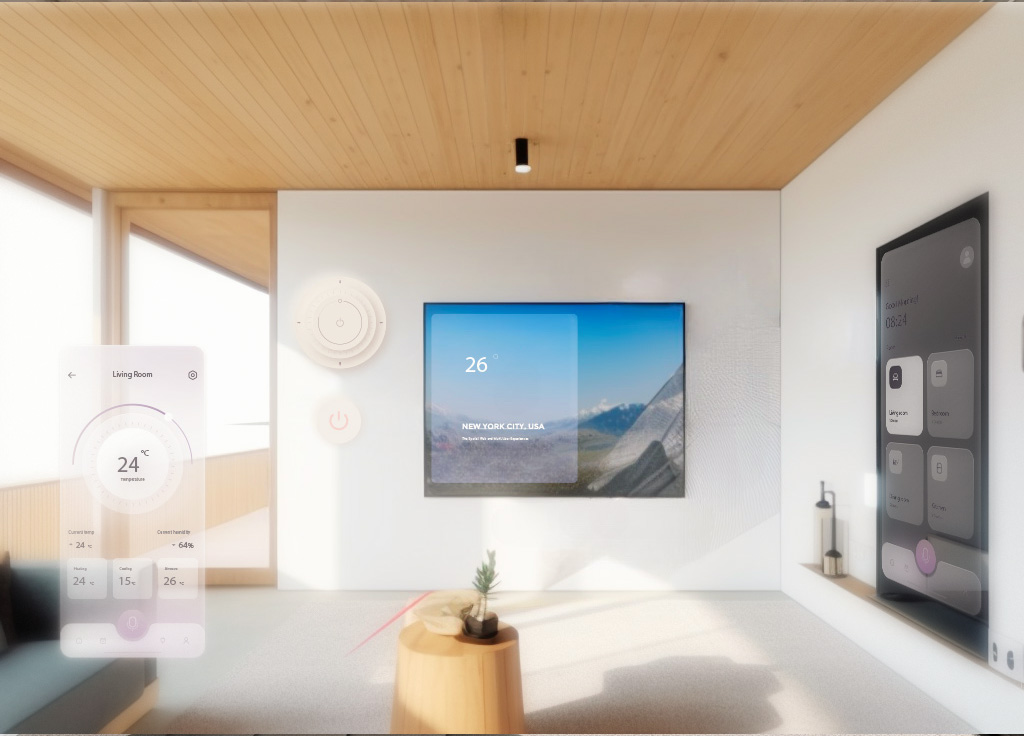

One of the critical components of the Spatial Web is its ability to support multi-user experiences. With the rise of wearables, smart glasses, AR / VR interfaces, and the IoT, the Spatial Web will integrate seamlessly into our physical environment, overlaying every conversation, road, object, conference room, and classroom with intuitively-presented data and AI-aided interaction. By allowing users to interact simultaneously within shared digital spaces, the Spatial Web opens new possibilities for collaboration, social interaction, and immersive experiences in properties search, transactions, and community-building.
C. The potential impact on the real estate industry
Imagine if sellers could walk a dozen potential buyers through a virtual open house without leaving their office, and then do the same thing multiple times a day for that and every other property in their portfolio. From virtual property tours and open houses to real-time collaboration during transactions, Web 3.0 innovations can streamline the selling processes, improve user experience, and foster a greater sense of community among potential buyers, sellers, and agents at a truly unprecedented scale.
III. Virtual Property Tours and Open Houses
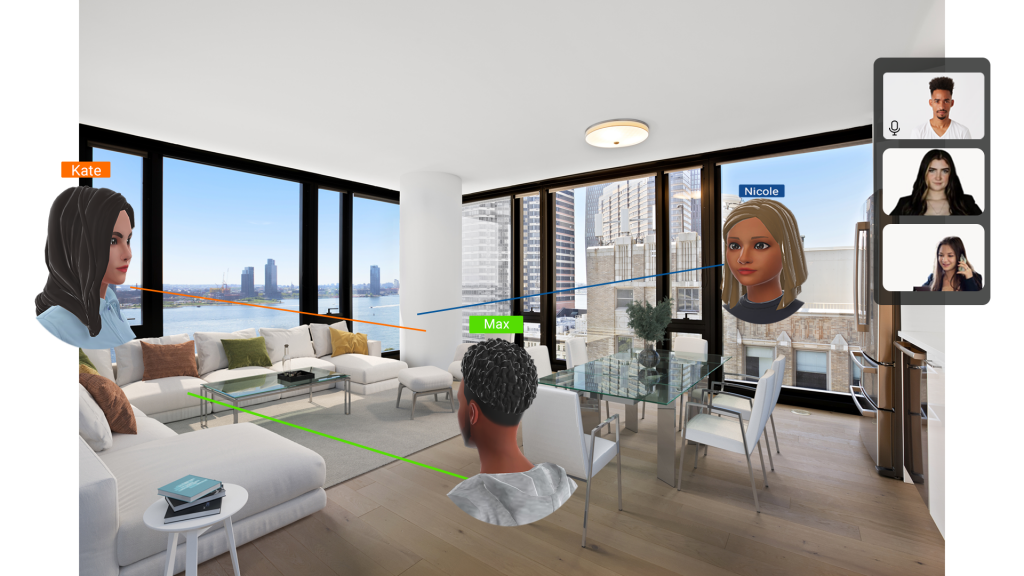

A. Interactive, multi-user virtual tours

Multi-user virtual tours take property exploration to a new level, allowing multiple users to navigate and experience a property simultaneously. Potential buyers can tour a property they are considering with family members, friends, or real estate agents, regardless of where everyone is located geographically. Users can communicate, discuss property features, and ask questions in real time while gaining valuable insights from the shared experience.

B. Advantages of virtual open houses
Virtual open houses offer a more efficient and cost-effective alternative to traditional in-person events. By enabling multiple users to attend an open house simultaneously, sellers and agents can reach a broader audience without the constraints of physical space and scheduling. Virtual open houses can be made available 24/7, allowing potential buyers to visit at their convenience and revisit the property as many times as they wish.
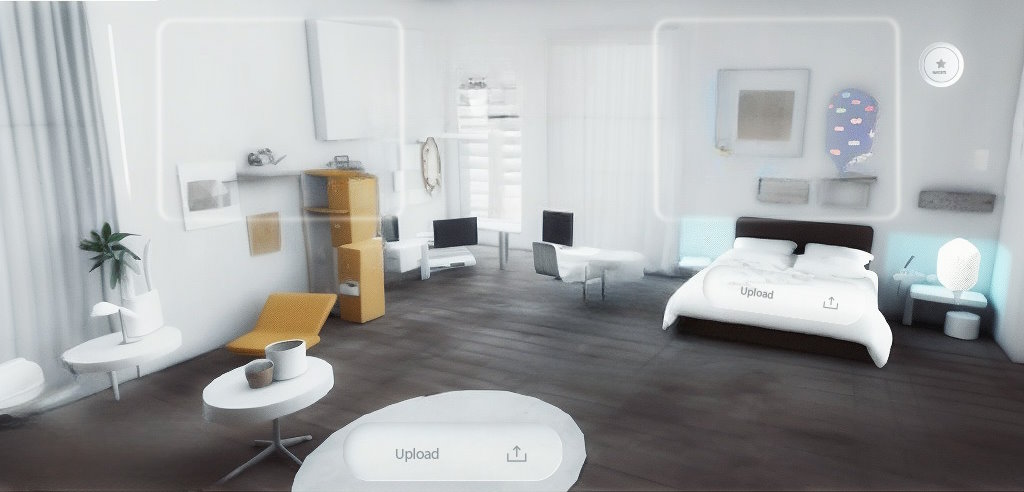

C. Enhanced property exploration and customization
Integrating multi-user experiences also allows users to customize their property exploration. Instead of relying on imagination, potential buyers can actually modify the property’s layout, furniture, and color schemes virtually and see how their preferences fit within the space. Not only does this interactivity engage buyers and help them make informed decisions, it also provides invaluable feedback to sellers and agents.
IV. Real-Time Collaboration in Real Estate Transactions
A. Virtual meetings with agents, buyers, and sellers
There was a time when issues had to be discussed in-person, and maybe even on-site. Now digital twin software like Matterport is eliminating most needs for in-person collaboration. Virtual meetings can either replace or complement in-person meetings, making it more convenient for buyers, sellers, and agents to discuss property details, negotiate terms, and address concerns seamlessly. This approach saves time, reduces travel expenses, and increases overall efficiency in the transaction process.
B. Real-time document sharing and contract negotiation
The integration of blockchain technology and smart contracts within the Spatial Web further streamline the transaction process. Real-time document sharing allows all parties to review, edit, and sign necessary documents collaboratively, ensuring transparency and reducing the risk of miscommunication. Smart contracts can automate various aspects of the transaction, such as escrow and property transfer, while providing a secure, decentralized record of the agreement.
C. Streamlining the closing process
Multi-user experiences enable parties to review and sign closing documents virtually, eliminating the need for physical paperwork, speeding up the process and reducing the potential for errors. Integrating blockchain technology can also provide a tamper-proof record of the transaction, ensuring the integrity and security of the closing process.
V. Augmented and Virtual Reality for Property Visualization

A. AR/VR integration in real estate platforms
The combined uses of AR/VR can provide immersive property visualizations, allowing potential buyers to experience a property as if they were physically present. This integration can create a more engaging and realistic experience, leading to better-informed decisions, increased user satisfaction, and widening your potential renter or buyer pool by eliminating geographic restrictions.

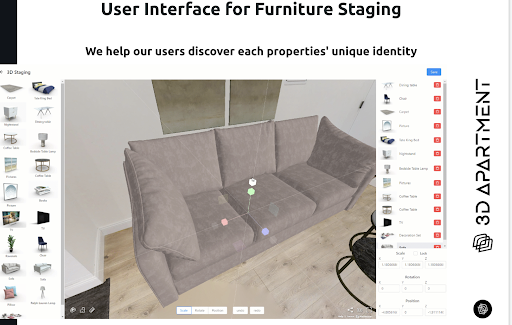
B. Immersive property staging and interior design
AR/VR technologies can also facilitate property staging and interior design by enabling users to visualize furniture, décor, and other design elements within a property. Multi-user experiences can allow potential buyers to collaborate with interior designers or other family members, experimenting with different layouts and styles in real-time. As users create their ideal living space, they can better envision themselves living in the property, which can both motivate the sale and increase the buyer’s satisfaction with their purchase.
C. Visualizing property development and construction projects
For property developers, architects, engineers and construction professionals, multi-user experiences and the Spatial Web can provide a powerful visualization tool for new projects. By creating virtual walkthroughs of proposed developments, stakeholders can collaborate in real-time, review designs, and make changes before construction begins – which saves time, reduces costs, and allows planners to address errors early in the development process.
VI. Building Virtual Communities and Social Engagement
A. Virtual neighborhood tours and community exploration
For buyers looking for a place to live, it’s not only what’s between the walls that count. The use of Spatial Web extends beyond individual properties, enabling potential buyers to virtually explore neighborhoods and the communities where they might potentially live. Users can navigate local amenities, such as parks, schools, and shopping centers, and even interact with other virtual visitors or residents. This immersive exploration can provide valuable insights into the local environment, helping buyers make more informed decisions about their future home.
B. Connecting potential buyers and residents
Real estate platforms can leverage multi-user experiences to foster social connections between potential buyers and existing residents. By integrating social networking features, users can engage in conversations, ask questions, and share experiences about the local community. This way, potential buyers get a better understanding of the neighborhood and develop a sense of belonging before they even move in.
C. Leveraging social media and virtual events for marketing
Hosting virtual events, such as open houses, community gatherings, or educational webinars lets agents engage with many potential buyers in a way that is both personal and interactive. Being able to share high-definition 360-degree view media to social media platforms amplifies potential reach and can even attract the curiosity—and interest—of people who may not have been in the market to purchase until they saw what they were missing.
VII. Challenges and Limitations
A. Technological barriers and infrastructure
Despite the potential benefits of multi-user experiences in real estate platforms, some technological barriers and infrastructure limitations may hinder widespread adoption. High-speed internet connections and advanced hardware are required to support the seamless integration of AR/VR and other Spatial Web technologies. Additionally, developing and maintaining these advanced platforms can be resource-intensive, potentially limiting access for smaller real estate businesses in the short-term.
B. Privacy and security concerns
Multi-user experiences and the Spatial Web involve the sharing of personal information and sensitive transaction details, which may give way to privacy and security concerns. Ensuring that platforms implement robust encryption and adhere to strict data protection regulations will be crucial to maintaining user trust and confidence in the technology.
C. Ensuring a seamless user experience
For multi-user experiences to be widely embraced, it is essential to provide a seamless and user-friendly experience. This includes intuitive navigation, high-quality visuals, and responsive customer support. Overcoming technical glitches and addressing accessibility concerns for users with disabilities will also play a critical role in the successful integration of these technologies within the real estate industry.
VIII. Conclusion:
Multi-user experiences on real estate platforms have the potential to rewrite the way we search, buy, and sell property. We are already seeing the effects of how Spatial Web, virtual tours, real-time collaboration, and immersive visualization can break down geographical barriers, streamline processes, and foster social connections between renters, buyers, sellers, and agents. By addressing the challenges associated with these technologies, we can unlock their full potential and create a more interconnected and engaging property market experience, foster community and connection among stakeholders, and ultimately reshape the industry for years to come.